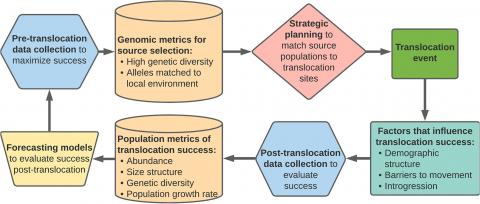
Whole-genome sequencing is revolutionizing our understanding of organismal biology, including adaptations likely to influence demographic performance in different environments. Excitement over the potential of genomics to inform population dynamics has prompted multiple conservation applications, including genomics-based decision-making for translocation efforts. Despite interest in applying genomics to improve translocations, there is a critical research gap: we lack an understanding of how genomic differences translate into population dynamics in the real world. We review how genomics and genetics data could be used to inform organismal performance, including examples of how adaptive and neutral loci have been quantified in a translocation context, and future applications. Next, we discuss three main drivers of population dynamics: demographic structure, spatial barriers to movement, and introgression, and their consequences for translocations informed by genomic data. Finally, we provide a practical guide to different types of models, including size-structured and spatial models, that could be modified to include genomics data. We then propose a framework to improve translocation success by repeatedly developing, selecting, and validating forecasting models. By integrating lab-based and field-collected data with model-driven research, our iterative framework could address long-standing challenges in restoration ecology, such as when selecting locally adapted genotypes will aid translocation of plants and animals.
Conceptual diagram of genomic integration with iterative translocation forecasting models. Data below provide one example of several types of relevant data.
| GEM3 author(s) | |
| Year published |
2021
|
| Journal |
Restoration Ecology
|
| DOI/URL | |
| GEM3 component |
Mechanisms
Modeling
|
| Mentions grant |
Yes
|